Orthognathic Surgery
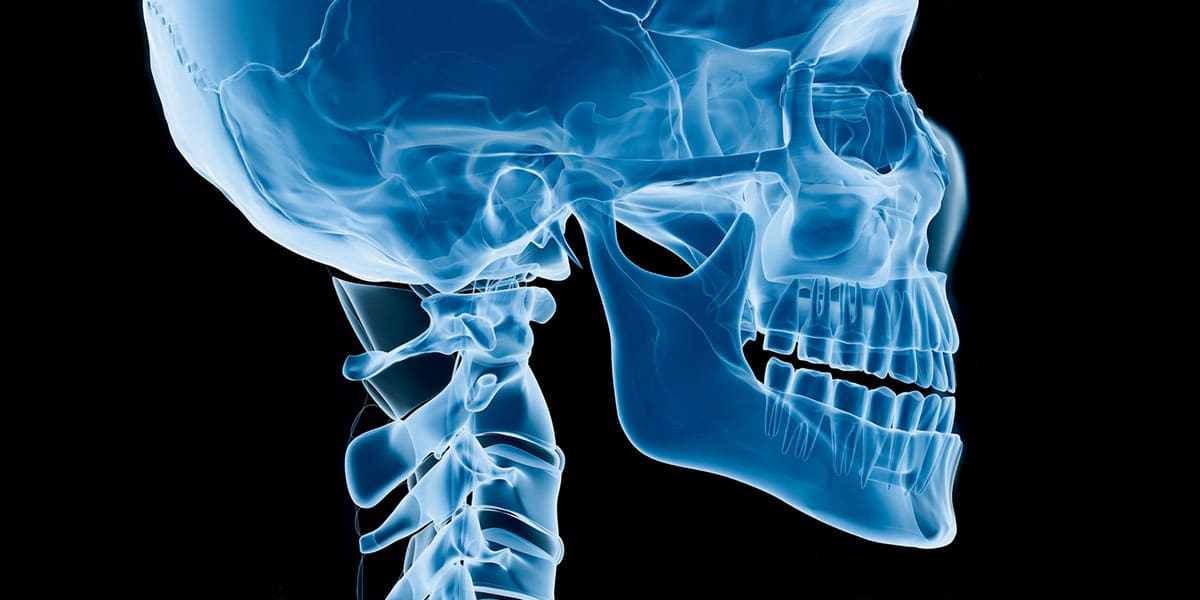
Orthognathic surgery is done to correct misalignments or other abnormalities in the upper and/or lower jaw. The surgery is performed to improve function and can specifically address problems with breathing, occlusion (bite) and chewing ability, and/or speaking that are due to poor jaw or tooth alignment. The surgery often dramatically affects appearance as well, although this is usually not the primary reason the surgery is performed.
Orthognathic surgery can involve procedures such as an osteotomy (bone cutting), bone grafts, distraction osteogenesis (stretching of the bone) and orthodontic (braces) care. Orthognathic correction is conducted in stages, and the course of treatment can last from a few months to a year or more.
In order to perform the procedure successfully, the jaw bone(s) will be repositioned in accordance with the patient's specific needs. Inconspicuous incisions are typically made inside the mouth in order to achieve the best aesthetic and functional results.
